1.Introduction to LET (Legal English teaching)
As legal English, or ELP (English for Legal Purpose), is one of the branches of ESP (English for Specific Purpose), the LET is different from that of general English teaching and certain for legal purpose, which is challenging for teachers who may be experts in English teaching but not in law, or vice versa. What is even more challenging is that multimodal information has gradually become increasingly employed in LET in China, as varieties of media are increasingly used in classroom teaching, but solutions to various problems in LET has not yet been found.
2. Methodology
The LET classroom observation is conducted from the perspective of multimodal discourse information processing, which was proposed and built up by Du Jinbang, and further developed and applied by Huai Yanmei.
2.1 MIC (Multimodal Information Corpus)
The use of MIC offers a feasible solution to multimodal information processing. MIC is an integral part of the Corpus for the Legal Information Processing System (CLIPS), which was built with the mechanism underlying the Tree Model of Discourse Information. With the help of the mechanism, MIC can facilitate the processing of multimodal information that has been discouralized. The basic techniques of MIC include how to categorize the multimodal information, how to process the multimodal information, and how to retrieve the multimodal information.
2.2 Class Modules based on discourse information
Whatever the teaching models employed, some modules of teaching are basic, for example, making preparations, delivering lectures, assessing achievements, and organizing class activities, as is shown in the following table.
| Preparation |
Lecture |
Assessment |
Activity |
| Identifying |
Presentation |
Production |
Presentation |
| Collecting |
Monitoring |
Processing |
Q & A |
| Classifying |
Guiding |
Responses |
discussion |
| Compiling |
Adapting |
Scoring |
Concluding |
| ... |
... |
... |
... |
2.3 Management of multimodal discourse information in Class
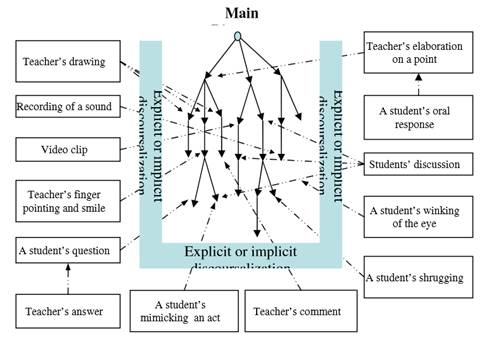
Although filled with varieties of multimodal information in LET, multimodal discourses can be extracted and stratified into main discourse and minor discourse. With the determination of the main discourse dominant in each class session, the teacher can derive a clear picture of the discourse system, i.e., the general structure of all the discourses centering around the dominant discourse. The interaction between all the discourses in the following graph incorporates the tree structure of discourse information, and with MIC techniques, the teacher can conveniently get instant access to the teaching materials prepared beforehand.
References
Du Jinbang. 2007. A Study of the Tree Information Structure of Legal Discourse. Modern Foreign Languages, 30(1): 40-50.
Du Jinbang. 2012. International Journal of Law, Language & Discourse. 2(4): 19-38.
Du Jinbang. 2013. International Journal of Legal English. 1(1): 23-47.
Huai Yanmei. 2013. The Proposal for PHD: A Study on Multimodal Information Processing in the Classroom Instruction of English for Legal Purpose. Guangdong University of Foreign Studies.
