Defining Culture
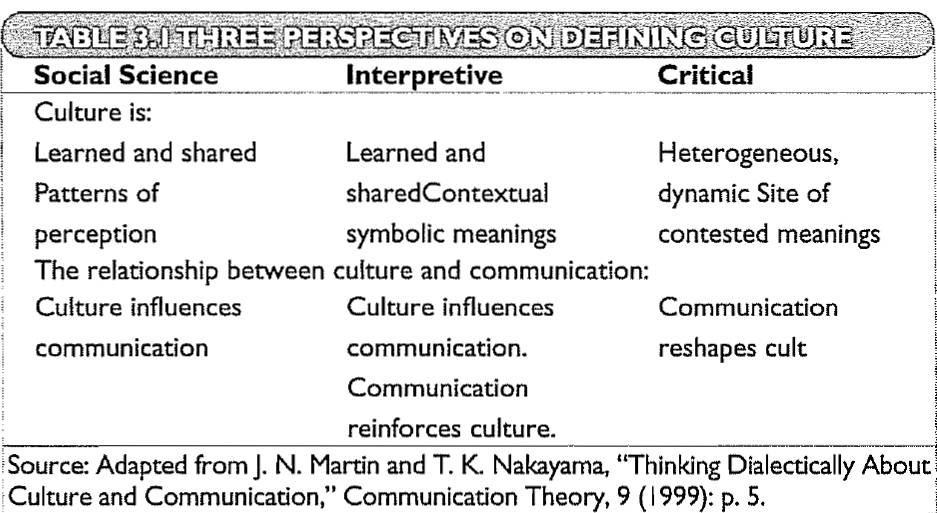
² Social Science Definition: Culture as learned, group-related perception
² Hofstede(1984): The programming of the mind
Every person carries within him patterns of thinking, feeling and potential acting which were learned throughout his lifetime.
² Singer(1987): Culture is a pattern of learned, group-related perception-including both verbal and nonverbal language attitudes, values, belief system, disbelief systems and behavior.
² Interpretive Definition: Culture as contextual symbolic pattern of meaning
² Geertz(1973):an historically transmitted pattern of meaning embodied in symbols, a system of inherited conceptions expressed in symbolic forms by means of which men communicate, perpetuate and develop their knowledge about and attitude toward life.
² Philipsen(1992):Culture refers to a socially constructed and historically transmitted pattern of symbols, meaning, premises, and rules.
² Critical Definition: Culture as heterogeneous, dynamic, and a contested zone
Main characteristics of culture
² Culture is manifested through different types of regularities, some of which are more explicit than others.
² Culture is associated with social groups, but no two individuals within a group share exactly the same cultural characteristics.
² Culture affects people’s behavior and interpretations of behavior.
² Culture is acquired and/or constructed through interaction with others.
Describing culture
² Dimensions of Cultural Variability: Geert Hofstede
³ Individualism vs. Collectivism
³ Power Distance: small vs. large
³ Uncertainty Avoidance: high vs. low
³ Masculinity vs. Femininity
² Schwartz’s value inventory
权利(power)、成就 (achievement)、享乐主义(hedonism)、鼓舞(stimulation)、自我引导(self-direction)、普遍主义(universalism)、仁爱(benevolence)、传统(tradition)、合乎规范(conformity)、安全(security)
² Kluckhohn & Strodtbeck’s Values Orientation Theory
² Nature of human nature对人性的看法
² Humanity and natural environment对自身与外部自然环境关系的看法
² Relating to other people对自身与他人之关系的看法
² Motive for behaving人的活动导向
² Space人的空间观念
² Time人的时间观念
² Hall's Behavioural Components of Culture
² Messages:Fast VS Slow
² Context: High VS Low
² Territoriality
² Personal Space
² Time:Monochronic VS Polychronic
² Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner’s Seven Dimensions of Culture
² Universalism VS Particularism普遍主义和特殊主义
² IndividualismVS Communitarianism个人主义和集体主义
² Neutral VS Emotional中性与情绪化
² Specific VS Diffuse具体专一与广泛扩散
² Achievement VS Ascription成就与归属
² Sequential time versus synchronous time.与同步
² Internal direction versus outer direction对环境的取向
Culture related theories
² Iceberg Model of Culture
文化冰山模式是最为人们熟知的文化模式之一,其主要研究焦点是组成文化的要素以及这些要素中显性的部分和隐性的部分。
² 这一理论把文化比喻成冰山:露出水面的只不过是冰山的一小部分,且这一部分需要隐藏于水下的部分作为支撑,而这一隐藏部分往往是重要的基础。
² 事实上,文化中存在某些显性的部分,例如:建筑、艺术、烹饪、音乐、语言等。但是文化中更为重要的基础部分则不易被察觉,例如:代表某一群体文化的历史、习俗、价值观以及对于空间、自然和时间的态度等。
² Jacques Demorgon and Markus Molz's Discussion of Culture
² Assimilation 同化:将外部世界归入我们头脑中现成的框架里
² Accommodation 融合:头脑中的框架随着外部世界信息的变化而调整
² 文化是关于在适应过程中如何在两个极端之间做出恰当的决定。文化的定位作用就是要将潜在行为的可能性限制到一个较小的范围内
² Face Negotiation Theory: Stella Ting-Toomey
How different cultures manage conflict and communicate.
Face Negotiation Theory
² The root of conflict is based on identity management on an individual and cultural level
² The various facets of individual and cultural identities are described as faces.
² Conflict occurs when that group or individual has their face threatened.
² In collectivist cultures, the face of the group is more important than the face of any individual in that group.
² In individualist cultures, the face of the individual is more important than the face of the group.
